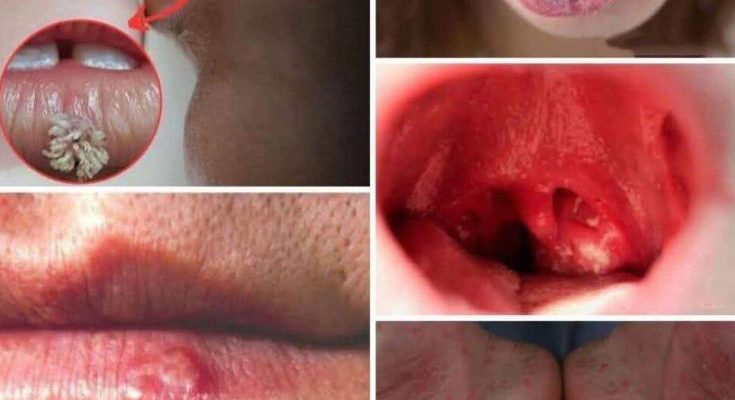
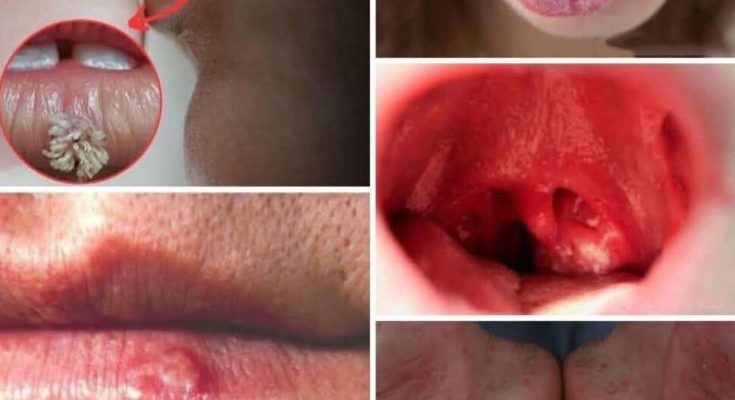
Imagine waking up one morning with a tiny sore in your mouth. Maybe you blame a sharp edge of food or a late-night snack. Days pass, and the sore stubbornly remains. Weeks go by, and instead of healing, it deepens. Most of us would brush it off—busy lives make ignoring minor issues far too easy. But sometimes, these little signs whisper warnings of something much larger.
Mouth cancer often begins with such subtle hints. It doesn’t burst into your life dramatically. It arrives quietly, hiding behind everyday discomforts. And because symptoms often appear late, many patients discover the illness only after it has reached the lymph nodes in the neck.
With more than 77,003 cases reported in India this year and 52,067 lives lost, the disease is far from rare. Understanding it—really understanding it—can make all the difference.

What Exactly Is Mouth Cancer?
Mouth cancer, or oral cancer, falls under the broader category of head and neck cancers. It tends to affect individuals over 40, particularly men, though anyone exposed to certain habits can develop it. The cancer can appear in many parts of the mouth, each location offering its own clues.
The Main Types Include:
Cancer of the lips
Cancer of the tongue
Inner cheek cancer
Gum cancer
Cancer of the floor of the mouth
Dentists and oncologists emphasize one point repeatedly: don’t wait for symptoms to worsen before seeking help. A quick examination twice a year can catch problems before they escalate.
Early Symptoms: The Ones We Often Ignore
One of the biggest challenges with oral cancer is that early symptoms often feel harmless. But when they linger, they deserve attention.
Here are the symptoms most connected to mouth cancer:
A non-healing ulcer or sore
Persistent mouth swelling
Bleeding without injury
A loose tooth without gum disease
Pain while swallowing or chewing
A new lump in the neck
Constant ear pain
Rapid weight loss
Numbness in the lips, chin, or face
Red or white patches inside the mouth
A dry, painful throat
Jaw stiffness or pain
Tongue soreness
It’s important to remember that many of these symptoms can arise from infections or minor issues. However, if they persist despite treatment, or if several symptoms appear at once, it’s essential to meet a dentist or doctor immediately.

Why Does Mouth Cancer Happen?
Like many serious illnesses, mouth cancer isn’t random. It has well-known causes, and understanding them helps you reduce your risk.
1. Smoking
The habit most strongly linked to oral cancer. Cigarettes, cigars, and pipes all expose the mouth to harmful chemicals.
2. Chewing Tobacco
Gutka, paan, zarda, khaini—no matter the form, smokeless tobacco is extremely dangerous. It is responsible for nearly 80% of oral cancer cases in India.
3. Alcohol Overuse
Heavy drinking weakens the lining of the mouth, making it more vulnerable to cancer-causing substances. When alcohol and tobacco combine, the risk rises sharply.
Stages: How Mouth Cancer Grows
Understanding the four stages of mouth cancer can help you understand why early detection matters so much.
Stage 1
A small tumor, less than 1 inch, with no spread.
Stage 2
A tumor between 1 and 2 inches, still confined to the primary area.
Stage 3
Either the tumor grows beyond 2 inches or spreads to nearby lymph nodes.
Stage 4
The most advanced stage, where cancer affects surrounding tissues or distant organs.
These stages guide doctors in choosing the most effective treatment plan.
Treatment Options: How Doctors Fight Mouth Cancer
Medical treatments today are powerful and varied. A specialist might choose one or combine several, depending on the individual case.
1. Surgery
Surgery removes the tumor completely. Surgeons may access it through the neck, jaw, or inside the mouth. After removal, the area is reconstructed using specialized techniques.
2. Radiation Therapy
Radiation targets cancer cells directly. Options include:
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)
Brachytherapy
These may be used alone or in combination with surgery or chemotherapy.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses potent drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. It’s often paired with radiation for stronger results.
4. Targeted Therapy
This approach focuses specifically on the abnormal cancer cells, preventing them from multiplying and spreading.
Important Facts Worth Knowing
Tobacco is the cause of 80% of mouth cancer cases.
The disease most often affects people aged 50 and above.
Men have significantly higher rates than women.
Early detection increases the survival rate to 82%.
Late detection reduces survival to 27%.
These statistics highlight one clear message: early action saves lives.
Protecting Yourself Starts With Awareness
Oral health is something many people neglect—until pain forces them to act. But mouth cancer thrives in that gap of inattention. Taking simple steps makes a huge difference:
Schedule dental checkups twice a year.
Quit tobacco completely.
Reduce alcohol intake.
Pay attention to changes inside your mouth.
Seek treatment immediately if symptoms persist.
If you notice signs that worry you, consulting an expert like Dr. Sajjan Rajpurohit, a trusted specialist in mouth cancer, can guide you toward the right care.